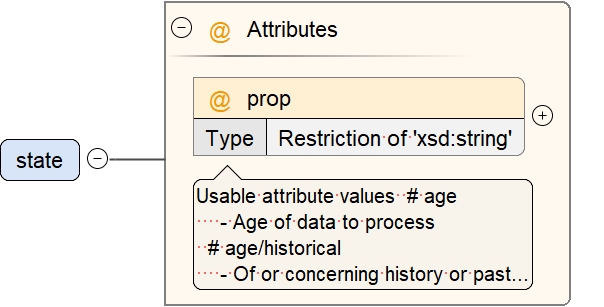
- Usable attribute values
- age
- Age of data to process
- age/historical
- Of or concerning history or past events
- age/historical/medieval
- Relating to the Middle Ages.
- age/contemporary
- Belonging to or occurring in the present
- age/ancient
- Belonging to the very distant past and no longer in existence.
- automation
-
Description coming soon.
- automation/manual
- Human interaction required
Examples:
Ground truthing
Related:
Performance evaluation
- automation/automated
- No interaction required
Examples:
OCR
Related:
Machine learning
- automation/assisted
- Some automation, but user interaction possible / required
Examples:
Auto-completion when typing
Related:
Trainable,
Interactive
- production-method
- Production method of physical document (e.g. paper document such as a book)
- production-method/manual
- E.g. handwritten
- production-method/machine
-
Description coming soon.
- production-method/machine/printed
-
Description coming soon.
- production-method/machine/printed/typeset
- Printed using typesetting method
- production-method/machine/printed/computer
- Printed from computer or other electronic device using an office or similar printer
- production-method/machine/typewritten
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type/data
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type/metadata
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type/metadata/quality
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type/metadata/quality/performance-info
-
Description coming soon.
- content-type/metadata/features
- Extracted features
Examples:
Word count of a text
Related:
Information extraction,
Machine learning
- content-type/metadata/structure
- Structure of an object of some sort
Examples:
Document structure,
Table structure
- content-type/metadata/structure/toc
- Table of contents of a book, newspaper etc.
- content-type/metadata/annotations
- Added data
- content-type/metadata/authorship
- Author attribution / information
- content-type/metadata/spatial
- Relating to space
- content-type/metadata/spatial/location
- Location or position
- content-type/settings
- E.g. tool configuration
- content-type/model
- A model for a concept.
Examples:
Page model to aid recognition
- content-type/lexicon
- A collection of data items organised / sorted in a certain way.
Lexicon: the vocabulary of a person, language, or branch of knowledge
- content-type/corpus
-
Corpus: a collection of written texts, especially the entire works of a particular
author or a body of writing on a particular subject.
Examples:
A text corpus,
An image database
- precision
-
Description coming soon.
- precision/ground-truth
- Ground truth is a term used in various fields to refer to information provided by
direct observation as opposed to information provided by inference.
Gold standard: the best available under reasonable conditions
- precision/measured
- Measured (precise)
Examples:
OCR performance measured using ground truth
- precision/estimated
- Estimated by machine or human (not precise)
- precision/random
- Random data of some sort.
Examples:
a random number between 1 and 6 (dice)
- precision/fuzzy
- Statistical data are not always precise numbers, or vectors, or categories. Real data
are frequently what is called fuzzy. Examples where this fuzziness is obvious are
quality of life data, environmental, biological, medical, sociological and economics
data. Also the results of measurements can be best described by using fuzzy numbers
and fuzzy vectors respectively.
- license
- Software or data usage licence
- license/free
-
Description coming soon.
- license/free/non-commercial
- Free for non-commercial use
- license/paid-for
-
Description coming soon.
- license/paid-for/pay-once
-
Description coming soon.
- license/paid-for/volume
-
Description coming soon.
- license/paid-for/subscription
-
Description coming soon.
- license/openSource
- Open-source software (OSS) is computer software with its source code made available
with a license in which the copyright holder provides the rights to study, change,
and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose.
Related:
Free / paid for
- platform
- Supported platform
- platform/windows
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/macos
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/linux
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/platform-independent
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/platform-independent/java
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/platform-independent/web
- Web service or web app
- platform/mobile
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/mobile/ios
-
Description coming soon.
- platform/mobile/android
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/textual
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/textual/annotated
- Textual content with annotations
- content-encoding/textual/natural-language
- Text represents natural language.
Examples:
A news article
Related:
- content-encoding/structured
- E.g. XML
- content-encoding/structured/tabular
- Content encoded in tabular form
Examples:
A tab-separated table with headings and values
- content-encoding/image
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/image/colour
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/image/bitonal
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/mathematical
-
Description coming soon.
- content-encoding/mathematical/vector-based
- E.g. polygonal
- content-encoding/mathematical/vector-based/stroke-based
-
Examples:
Online handwriting
- content-encoding/mathematical/polygonal
-
Description coming soon.
- activityDomain
- General domain, research field or specific processing strategy of a workflow activity.
Examples:
An activity for automated number plate recognition could be labelled with "OCR" domain.
Related:
"Topic" of a data object
- activityDomain/computing
- Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating a
mathematical sequence of steps known as an algorithm — e.g. through computers.
Examples:
Any activity in document image analysis is from the domain of computing. Only steps
such as physical document restoration should be excluded.
Related:
Data object "topic" such as Engineering
- activityDomain/computing/visual
- Visual computing is a generic term for all computer science disciplines handling with
images and 3D models, i.e. computer graphics, image processing, visualization, computer
vision, virtual and augmented reality, video processing, but also includes aspects
of pattern recognition, human computer interaction, machine learning and digital libraries.
Examples:
See above
Related:
"Machine Learning" (separate label type)
- activityDomain/computing/visual/imgVidProc
- Image processing is processing of images using mathematical operations by using any
form of signal processing for which the input is an image, a series of images, or
a video, such as a photograph or video frame.
Video processing is a particular case of signal processing, which often employs video
filters and where the input and output signals are video files or video streams.
Examples:
Binarisation of a colour image
Related:
Content analysis (for information extraction)
Computer graphics (for visualisation)
- activityDomain/computing/visual/imgVidProc/geometric
- Affine transsformation or other geometric operation applied to an image / video.
An affine transformation is an important class of linear 2-D geometric transformations
which maps variables (e.g. pixel intensity values located at position Eqn:eqnxy1 in
an input image) into new variables (e.g. Eqn:eqnxy2 in an output image) by applying
a linear combination of translation, rotation, scaling and/or shearing (i.e. non-uniform
scaling in some directions) operations.
Examples:
Rotation, dewarping
Related:
Pixel-based operations
- activityDomain/computing/visual/imgVidProc/pixel-based
- Any image operation on pixel-level
Examples:
Binarisation, morphological operations
Related:
Geometric processing
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition
- Content analysis is "a wide and heterogeneous set of manual or computer-assisted techniques
for contextualized interpretations of documents produced by communication processes
in the strict sense of that phrase (any kind of text, written, iconic, multimedia,
etc.) or signification processes (traces and artifacts), having as ultimate goal the
production of valid and trustworthy inferences."
Examples:
Text recognition / OCR
Related:
Text processing (separate categoty)
Performance evaluation (separate categoty)
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/text
- Translation of any kind of depicted symbols to machine readable format
Examples:
OCR
Mathematical equation recognition
Related:
Text processing (separate category)
Table recognition
Map reading
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/text/ocr
- Optical character recognition (optical character reader, OCR) is the mechanical or
electronic conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded
text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example
the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed
on an image (for example from a television broadcast).
Examples:
Number plate reading
Related:
Mathematical equation recognition
Map reading
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/text/maths
- Specialised recognition of mathematical equations / formulas.
Examples:
Equations in scientific papers
Related:
OCR
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/text/date
- Specialised recognition of dates and times
Examples:
Date printed on newspaper page
Related:
OCR
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/tables
- The recognition of table/form structure and/or contents.
Examples:
Stock exchange data in a newspaper,
Filled in questionnaire form
Related:
OCR
Object / shape recognition (e.g. table separator detection)
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/charts
- Recognition or analysis of data charts.
Examples:
Pie chart,
Bar chart,
Graphs
Related:
OCR,
Object / shape recognition
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/maps
- Recognition and analysis of maps or plans of any kind.
Examples:
Floor plans,
Engineering drawings,
Geographical maps
Related:
OCR,
Object / shape recognition
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/shape
- Object recognition is a process for identifying a specific object in a digital image
or video. Object recognition algorithms rely on matching, learning, or pattern recognition
algorithms using appearance-based or feature-based techniques. Common techniques include
edges, gradients, Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG), Haar wavelets, and linear
binary patterns.
Examples:
Logo recognition
Fingerprint reading
Related:
Machine learning,
Text and symbol recognition
Forensic studies
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/shape/face
- A facial recognition system is a computer application capable of identifying or verifying
a person from a digital image or a video frame from a video source. One of the ways
to do this is by comparing selected facial features from the image and a facial database.
Examples:
Smartphone unlocking via detection of owner's face
Related:
Machine learning (separate category)
- activityDomain/computing/visual/analysisRecognition/layoutAnalysis
- In computer vision, document layout analysis is the process of identifying and categorizing
the regions of interest in the scanned image of a text document. A reading system
requires the segmentation of text zones from non-textual ones and the arrangement
in their correct reading order.
Examples:
Page layout analysis (segmentation into regions, classification into text, graphic,
table etc.)
Related:
"OCR": Often used as a synonym for layout analysis and text recognition, but strictly
only the text recognition component.
- activityDomain/computing/visual/graphics
- Computer graphics are pictures and movies created using computers - usually referring
to image data created by a computer specifically with help from specialized graphical
hardware and software.
Example:
Text rendering
Related:
Presentation / visualisation (part of Data Creation / Transformation)
- activityDomain/computing/text
- In computing, the term text processing refers to the discipline of mechanizing the
creation or manipulation of electronic text. Text usually refers to all the alphanumeric
characters specified on the keyboard of the person performing the mechanization, but
in general text here means the abstraction layer that is one layer above the standard
character encoding of the target text. The term processing refers to automated (or
mechanized) processing, as opposed to the same manipulation done manually.
Text processing involves computer commands which invoke content, content changes,
and cursor movement, for example to
- search and replace
- format
- generate a processed report of the content of, or
- filter a file or report of a text file.
Related:
Text recognition (Visual Computing)
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage
- Natural language processing (NLP) is a field of computer science, artificial intelligence,
and computational linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and
human (natural) languages. As such, NLP is related to the area of human–computer interaction.
Many challenges in NLP involve: natural language understanding, enabling computers
to derive meaning from human or natural language input; and others involve natural
language generation.
Examples:
Digital assistants (e.g. in smartphones)
Related:
OCR
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage/identification
- In natural language processing, language identification or language guessing is the
problem of determining which natural language given content is in.
Examples:
Language identification to select a dictionary for OCR applications
Related:
OCR
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage/sentiment
- Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language
processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective
information in source materials.
Examples:
A basic task in sentiment analysis is classifying the polarity of a given text at
the document, sentence, or feature/aspect level — whether the expressed opinion in
a document, a sentence or an entity feature/aspect is positive, negative, or neutral.
Related:
Summarising
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage/summarising
- Automatic summarization is the process of reducing a text document with a computer
program in order to create a summary that retains the most important points of the
original document. Technologies that can make a coherent summary take into account
variables such as length, writing style and syntax.
Examples:
Automatic summary of a news article
Related:
Sentiment mining
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage/partOfSpeech
- In corpus linguistics, part-of-speech tagging (POS tagging or POST), also called grammatical
tagging or word-category disambiguation, is the process of marking up a word in a
text (corpus) as corresponding to a particular part of speech, based on both its definition
and its context—i.e., its relationship with adjacent and related words in a phrase,
sentence, or paragraph.
Examples:
A simplified form of this is commonly taught to school-age children, in the identification
of words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc.
Related:
Named entity recognition,
Tokenisation (as part of Data creation / transformation)
- activityDomain/computing/text/naturalLanguage/namedEntities
- Named-entity recognition (NER) (also known as entity identification, entity chunking
and entity extraction) is a subtask of information extraction that seeks to locate
and classify named entities in text into pre-defined categories such as the names
of persons, organizations, locations, expressions of times, quantities, monetary values,
percentages, etc.
Related:
Part-of-speech tagging
Summarising
- activityDomain/computing/machineLearning
- Machine learning is a subfield of computer science[1] that evolved from the study
of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence.
In 1959, Arthur Samuel defined machine learning as a "Field of study that gives computers
the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed". Machine learning explores
the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions
on data.
Examples:
Decision tree learning,
Artificial neural networks
Related:
Content analysis and recognition
- activityDomain/computing/informationManagement
- Information management (IM) concerns a cycle of organisational activity: the acquisition
of information from one or more sources, the custodianship and the distribution of
that information to those who need it, and its ultimate disposition through archiving
or deletion.
Data management comprises all the disciplines related to managing data as a valuable
resource.
Examples:
Data access,
Data security
Document management system
Related:
Visualistation (as part of Data Creation / Transformation)
- activityDomain/computing/informationManagement/retrieval
- Data retrieval means obtaining data from a database management system such as ODBMS.
In this case, it is considered that data is represented in a structured way, and there
is no ambiguity in data. In order to retrieve the desired data the user present a
set of criteria by a query.
Examples:
Retrieval of image from image database using pattern matching
Related:
Visualisation
- activityDomain/computing/performanceEval
- Measuring the performance of a given software system or method, returning for instance
a quality value.
Examples:
OCR accuracy measurement
Related:
Information extraction
Pattern matching
- activityDomain/computing/performanceEval/comparative
- Basic comparison of software systems or methods to decide which is better under given
circumstances.
Examples:
Number of correctly recognised words of two OCR engines
Related:
Information extraction
Ground truth
- activityDomain/computing/performanceEval/in-depth
- Performance analysis providing detail on the evaluation result in order to be able
to understand the result and improve the methods / systems under investigation.
Examples:
Region-based layout analysis performance with merges, splits, misses, false detections
etc.,
OCR accuracy with recognition statistics per character class
Related:
Information retrieval
- activityDomain/computing/forensics
- Forensic science is the application of science to criminal and civil laws. Forensic
scientists collect, preserve, and analyze scientific evidence during the course of
an investigation.
Examples:
Document verification / counterfeit detection
Related:
Face recognition
- processingLevel
- Distinction between low-level data processing (e.g. using a mathematical formula)
and high-level processing that entails some form of recognition, reasoning or matching.
- processingLevel/low-level
- Data processing involving basic conversion, application of mathematical formulas or
similar
Examples:
Image thresholding
Image smoothing
Text chunking (e.g. splitting into words)
Related:
Several visual computing approaches
- processingLevel/high-level
- Processing that entails some form of recognition, reasoning or matching, for example.
Examples:
OCR
Face recognition
Related:
Natural language processing,
Content analysis and recognition
- processingLevel/high-level/detection
- Methods involving some form of detection, identification, location or matching.
Examples:
Writer identification,
Logo detection
Related:
Object recognition,
OCR,
Machine learning
- processingLevel/high-level/detection/verification
- Authentication (from Greek: αὐθεντικός authentikos, "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης
authentes, "author") is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a single
piece of data (a datum) claimed true by an entity. In contrast with identification
which refers to the act of stating or otherwise indicating a claim purportedly attesting
to a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of actually confirming
that identity.
Examples:
Signature verification
Related:
Forensic studies,
Content analysis and recognition
- processingLevel/high-level/classification
- In machine learning and statistics, classification is the problem of identifying to
which of a set of categories (sub-populations) a new observation belongs, on the basis
of a training set of data containing observations (or instances) whose category membership
is known.
Pattern recognition is a branch of machine learning that focuses on the recognition
of patterns and regularities in data, although it is in some cases considered to be
nearly synonymous with machine learning.
Examples:
OCR
Related:
Machine learning,
Content analysis and recognition
- processingLevel/high-level/understanding
- Highest level of processing including reasoning based on the actual meaning of the
data that is beaing processed.
Examples:
Natural language understanding
Related:
Machine learning,
Content analysis and recognition,
Natural language processing
- dataTransformation
- Any action to creates or transforms data.
Examples:
Image acquisition,
conversion,
Text tokenisation,
Annotation,
Extraction
- dataTransformation/acquisition
- Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real world physical
conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can
be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms
DAS or DAQ, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing.
The components of data acquisition systems include:
Sensors, to convert physical parameters to electrical signals.
Signal conditioning circuitry, to convert sensor signals into a form that can be converted
to digital values.
Analog-to-digital converters, to convert conditioned sensor signals to digital values.
Related:
Conversion
Retrieval
- dataTransformation/conversion
- Data conversion is the conversion of computer data from one format to another.
Examples:
JPG image to PNG image,
UTF-8 encoded text to ASCII
Related:
Low-level processing
- dataTransformation/segmentation
- Splitting data into distinct parts or demarking the points where to split.
Examples:
Document page segmentation,
Image segmentation,
Foreground-background separation,
Text tokeinsation / chunking
Related:
Content analysis / recognition
Annotation / labelling
- dataTransformation/enhancement
- Removal of unwanted parts of data or adding/correcting data to improve readability,
quality. Pre- or postprocessing of some kind.
Examples:
Noise removal in images,
Geometric correction,
Spelling correction,
Watermark removal,
Text restoration
Related:
Low-level processing
- dataTransformation/enrichment
- Adding data to increase information content
Examples:
Adding metadata
Related:
Part-of-speech tagging
- dataTransformation/enrichment/annotation
- Localised addition of information.
Examples:
Part-of-speech tagging,
Named entity tagging,
Page layout annotation (regions etc.)
Related:
Segmentation
- dataTransformation/extraction
- Information extraction (IE) is the task of automatically extracting structured information
from unstructured and/or semi-structured machine-readable documents. In most of the
cases this activity concerns processing human language texts by means of natural language
processing (NLP).
Examples:
Language and vocabulary analysis,
Image understanding
Related:
High-level processing
Content analysis and recognition
- dataTransformation/visualisation
- Information visualisation is the study of (interactive) visual representations of
abstract data to reinforce human cognition. The abstract data include both numerical
and non-numerical data, such as text and geographic information.
Examples:
Text rendering
Chart creation
Related:
Conversion
Computer graphics
- adaptability
- How well can the activity adapt to different circumstances.
Examples:
Trainable method,
Interactive system
- adaptability/configurable
- A method that can be configured in some way to allow the explicit adaption to different
use cases.
Examples:
OCR with settings for language, font etc.
Related:
Interactive
Generic / unconstraint
- adaptability/trainable
- A method that can be trained by examples.
Examples:
OCR training to support a new type of font
Related:
Configurable,
Interactive,
Generic / unconstraint
- adaptability/trainable/supervised
- Supervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function from labeled
training data.[1] The training data consist of a set of training examples. In supervised
learning, each example is a pair consisting of an input object (typically a vector)
and a desired output value (also called the supervisory signal). A supervised learning
algorithm analyzes the training data and produces an inferred function, which can
be used for mapping new examples.
Examples:
Labelled character images for training an OCR engine
Related:
Configurable
Interactive
- adaptability/trainable/unsupervised
- Unsupervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function to describe
hidden structure from unlabeled data. Since the examples given to the learner are
unlabeled, there is no error or reward signal to evaluate a potential solution. This
distinguishes unsupervised learning from supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
Examples:
Clustering
Related:
Machine learning
- adaptability/interactive
- A method that adapts according to user interaction.
Examples:
Dictionary expansion during spell checking
Related:
Configurable,
Trainable
- adaptability/generic
- Method with wide applicability which therefore may not need to be trained or configured.
Examples:
Google multi-language OCR
Related:
Trainable,
Configurable
- maturity
- System / method/ algorithm maturity.
Examples:
Prototype,
Production system
Related:
Licence
- maturity/stable
- A stable release is available
- maturity/experimental
- Experimental, in development, prototype
- maturity/industrial
- Production-strength method / system that is reliable, tested, and robust
- originalSource
- Disregarding the current form of the data, where does it originate from, what was
the original medium?
- originalSource/produced
- Data that has been composed, created, produced or rendered in some form.
Examples:
Book,
Website
Related:
Content Encoding
- originalSource/produced/physical
- The data was orininally part of a physical medium
Examples:
Newspaper
Whiteboard writing
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/paper
- The data was originally produced on paper
Example:
Printed magazine
Related:
Age
- originalSource/produced/physical/paper/book
- A paper book
Examples:
Notebook,
Novel
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/paper/newspaper
- A printed newspaper
Examples:
The Guardian
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/paper/magazine
- A printed magazine.
Usyually with more complex layout and formatting in comparison to books or newspapers.
Examples:
Time magazine
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/paper/journal
- A printed journal
Examples:
Science journal
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/whiteboard
- The data was originally produced on a whiteboard / flipchart / blackboard
Examples:
Whiteboard bullet points from a meeting
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/physical/poster
- A poster or board of some kind
Examples:
A poster for a research paper
Related:
Physical production method
- originalSource/produced/virtual
- The data was created in / for the virtual space (digital)
Examples:
Word processor document
Related:
Content encoding
- originalSource/produced/virtual/www
- The data was created for the Internet.
Examples:
Wikipedia page
Related:
Data conversion,
Visualisation
- originalSource/captured
- Data captured from the real world / the environment
Examples:
Photograph of a street
Related:
Acquisition
- originalSource/captured/scenes
- Scenes captured from the world
Examples:
A picture of a room with people
Related:
Acquisition
- originalSource/captured/scenes/3D
- Threedimensional scenes captured somehow
- acquisition
- Involved methods that lead from the source medium to the current state / format
Examples:
Scanning,
Photocopying
Related:
Physical production method,
Source medium
- acquisition/analogToDigital
- Conversion from any form of analog or physical data / medium to digital form.
Examples:
Digital photography,
Scanning
Related:
Source medium
- acquisition/analogToDigital/scanning
- Capturing with digital scanner
Examples:
Flatbed scanner
Related:
Acquisition
- acquisition/analogToDigital/camera
- Camera-based digitisation
Examples:
Overhead scanner,
Smartphone document capture
Related:
Acquisition method
- acquisition/copied
- Replicated in some way
- acquisition/copied/photocopy
- A document that was photocopied at some point
- acquisition/copied/carbon-copy
- The document is a carbon copy
- acquisition/copied/microfilm
- The document copied to microfilm or microfiche at some point
- acquisition/copied/fax
- The document was faxed (using a fax machine)
- acquisition/synthesis
- The combination of components or elements to form a connected whole
Examples:
Artificial ground truth (e.g. a synthetic newspaper page)
Related:
Acquisition
Source medium
- contentOfInterest
- Source / target content. What is the interesting bit in the data at hand.
- contentOfInterest/visual
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/text
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/graphical
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/graphical/separator
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/graphical/barcode
- A barcode is a machine-readable representation of data relating to the object to which
it is attached. Originally barcodes systematically represented data by varying the
widths and spacings of parallel lines, and may be referred to as linear or one-dimensional
(1D). Later two-dimensional (2D) codes were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons
and other geometric patterns in two dimensions, usually called barcodes although they
do not use bars as such. Barcodes originally were scanned by special optical scanners
called barcode readers. Later applications software became available for devices that
could read images, such as smartphones with cameras.
Examples:
- Barcode on a product
- QR code representing a weblink
- contentOfInterest/visual/image
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/image/photograph
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/image/photograph/person
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/image/photograph/person/face
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/image/drawing
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/tables
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/charts
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/maps
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/maths
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/chem
-
Description coming soon.
- contentOfInterest/visual/composite/music
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical
- E.g. segmentation
- granularity/physical/document-related
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/document-related/page
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/document-related/region
- Region, zone, block
- granularity/physical/document-related/text-line
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/document-related/word
- Word or partial word, if separated by line break, for example
- granularity/physical/document-related/glyph
- In typography, a glyph is an elemental symbol within an agreed set of symbols, intended
to represent a readable character for the purposes of writing
- granularity/physical/document-related/double-page
- Two facing pages (e.g. in book)
- granularity/physical/natural-language
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/natural-language/sentence
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/natural-language/token
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/physical/natural-language/syllable
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/document-related
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/document-related/document
- A complete document
Examples:
Book
- granularity/logical/document-related/chapter
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/document-related/section
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/document-related/article
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/document-related/paragraph
-
Description coming soon.
- granularity/logical/table
- A table with columns and rows
- granularity/logical/table/column
- Table column
- granularity/logical/table/row
- Table row
- granularity/logical/table/cell
- Table cell
- condition
- Degradation, aging, damage etc.
- condition/noise
-
Description coming soon.
- condition/noise/speckles
- Speckle-like noise
- condition/noise/speckles/salt-and-pepper
- Small, bright and dark dot-like noise
- condition/noise/clutter
- Larger noise 'objects'
- condition/noise/clutter/thresholding-related
- Image thresholding / binarisation-related noise
- condition/production-related
- Conditions introduced during the production of the medium / object
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics
- Document-related characteristics
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/pasted-clippings
- Paper clippings pasted onto a page
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/textured-paper
- Paper with a visible texture
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/uneven-character-spacing
- Intra-word and inter-word character spacing is not uniform
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/narrow-border
- The content of a page reaches very close to the page border or even touches it
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/low-contrast
- The contrast between the paper and the page content is very low
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/halftoning
- Dot-based halftoning printing technique was used (to emulate more colours / grey tones)
- condition/production-related/document-characteristics/dithering
- Dithering printing technique was used (added randomness to avoid unwanted patterns)
- condition/production-related/document-faults
- Fault introduced during document production
- condition/production-related/document-faults/bleed-through
- Ink bled through from back of page
- condition/production-related/document-faults/ink-from-facing
- Ink from facing page was transferred to this page
- condition/production-related/document-faults/smeared-ink
- Ink was smeared after printing / writing
- condition/production-related/document-faults/touching-chars
- Independent characters are touching due to printing issues
- condition/production-related/document-faults/touching-chars/horizontally
- Neighbouring characters within one text line are touching
- condition/production-related/document-faults/touching-chars/vertically
- Characters from neighbouring text lines are touching each other
- condition/production-related/document-faults/uneven-ink-distrib
- The ink was not distributed properly during printing, leading to unwanted empty or
faint regions
- condition/production-related/document-faults/filled-in-chars
- Gaps or holes in characters are filled in (e.g. due to too much ink)
- condition/production-related/document-faults/sort-shoulder-artefacts
- Sort shoulder parts touched the paper during printing, leading to visible artefacts
around characters
- condition/production-related/document-faults/broken-chars
- Some print characters were broken (bits missing) leading to repeated visible defects
- condition/production-related/document-faults/faint-chars
- Faint individual characters, e.g. when not using enough force during typewriting
- condition/production-related/document-faults/blurred-chars
- Blurred characters due to production issues
- condition/production-related/document-faults/non-straight-text-lines
- Text lines were not printed straight (printing issue / limitation)
- condition/wear
-
Description coming soon.
- condition/wear/medium-damage
- The medium (e.g. paper) is damaged in some way
- condition/wear/medium-damage/folds
- E.g. paper folds
- condition/wear/medium-damage/tears
- Medium is torn
- condition/wear/medium-damage/holes
- Any kind of holes in the medium
- condition/wear/medium-damage/holes/punch-holes
- Punch holes visible
- condition/wear/medium-damage/holes/unintended
- Holes / missing parts in the medium due to damage
- condition/wear/medium-damage/missing-parts
- Whole parts of the medium are missing (e.g. torn off)
- condition/wear/medium-damage/stains
- Noticeable stains on medium
- condition/wear/medium-damage/scratches
- E.g. microfilm scratches
- condition/wear/medium-damage/staples
- Visible staples
- condition/wear/additions
- Things added to the medium during use
- condition/wear/additions/repairs
- The medium was visibly repaired
- condition/wear/additions/repairs/paper-repairs
- Paper was reapaired (e.g. with patches)
- condition/wear/additions/repairs/clear-tape
- Clear tape, visible through replections or darker colour
- condition/wear/additions/informative
- Additions containing information
- condition/wear/additions/informative/annotations
- Annotations regarding the content
- condition/wear/additions/informative/stamps
- The medium was stamped
- condition/wear/additions/corrections
- Content corrections
- condition/wear/additions/corrections/manual
- E.g. handwritten corrections of printed content
- condition/ageing
- Ageing or preservation-related issues
- condition/ageing/warping
- Arbitrary warping (e.g. due to moisture)
- condition/ageing/discolouration
- Discolouration of the medium of any kind
- condition/ageing/discolouration/global
- E.g. yellowish teint
- condition/ageing/discolouration/edges
- Local discolouration of the edges of the medium
- condition/ageing/disintegraion
- Disintegration of medium
- condition/ageing/disintegraion/uneven-edges
- Uneven medium edges due to disintegration
- condition/ageing/mould
- Visible damage through mould
- condition/ageing/faded-content
- Faded content (e.g. due to sunlight)
- condition/acquisition
-
Description coming soon.
- condition/acquisition/geometric
- Geometric distortions etc.
- condition/acquisition/geometric/skew
- Skew / rotation
- condition/acquisition/geometric/skew/global
- The whole page is skewed
- condition/acquisition/geometric/skew/non-uniform
- Non-uniform skew, e.g. due to faulty scan feed
- condition/acquisition/geometric/90-degree-rotation
- Page rotated 90 degree left or right
- condition/acquisition/geometric/upside-down
- The object is represented upside down (e.g. scanned the wrong way around)
- condition/acquisition/geometric/perspective-distortions
- Perspective distortions (e.g. due to camera-based acquisition)
- condition/acquisition/geometric/page-curl
- Visible page curl (e.g. book scanning)
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background
- Content- or background-related issues
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/incomplete-capture
- Not the whole content was captured during acquisition or copying
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/tight-margins
- Tight / narrow margins
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects
- Foreign objects visible
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/preceeding-or-proceeding
- Part of preceeding or succeeding object included (e.g. other page)
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/medium-structure
- Medium structure visible (e.g. book cover)
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/clips
- Paper clips visible
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/fingers
- Fingers visible
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/insects
- Insects visible
- condition/acquisition/content-or-background/included-objects/background
- Unwanted background visible (e.g. scanner bed)
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws
- Scanning or reproduction method flaws / issues
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging
- Imaging-related flaws
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/show-through
- Parts of other page showing through (e.g. due to thin paper)
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/uneven-illumination
- Uneven illumination leading to brightness or contrast variations
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/uneven-illumination/shadows
- Shadows visible
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/out-of-focus
- Object was not properly focused leading to blur
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/low-contrast
- Low image contrast
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/missing-content
- Some of the original content is missing or changed
- condition/acquisition/method-flaws/imaging/missing-content/thresholding
- Content or information loss due to thresholding / binaristaion
- data-attributes
-
Description coming soon.
- data-attributes/language
- Language(s) of data
- data-attributes/language/natural
- E.g. a spoken language
- data-attributes/language/natural/english
- English language
- data-attributes/language/mixed
- More than one language used
- data-attributes/document-related
- Document attributes
- data-attributes/document-related/visual
- Any visual properties / attributes
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text
- Text attributes
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/script
- Text script
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/script/latin
- Latin script
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/script/braille
- Braille script
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font
- Font attributes
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/cursive
- Cursive font (italics or handwritten)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/monospace
- Monospace font (all characters have the same width)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/typeface
- General typeface or hand
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/typeface/blackletter
- Blackletter, gothic, Fraktur
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/typeface/antiqua
- Antiqua font (more modern)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/typeface/manuscript
- Print-like manuscript font
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/decorated
- Text decorations to highlight or beautify
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/decorated/flourishes
- Flourishes added to the characters
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/decorated/multi-colour
- Multiple colours used for text (e.g. in one text line)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/decorated/reverse-video
- Dark background, bright text colour
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/multi-font
- Multiple fonts used
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/multi-font/typefaces
- More than one typeface used
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/font/multi-font/font-sizes
- More than one font size used
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/text/drop-caps
- Drap capitals (large capitals at beginning of paragraph)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/columns
- The content is arranged in columns or one column
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/columns/one
- One-column text
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/columns/two
- Two-column text
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/columns/multiple
- Multi-column text (more than two)
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/rotated-content
- Some content is rotated with respect to other content
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/complex-background
- Background not just plain white / colour
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/complex-background/watermarks
- Watermark(s) in background
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/complex-background/impressions
- Impressions / embossings visible
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/illustrations
- Illustrations in content
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/illustrations/multi-colour
- Multi-colour illustrations in content
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/decorations
- Decorations of some kind
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/decorations/frames
- Some content enclosed in frames or borders
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/line-art
- Line drawings / line art
- data-attributes/document-related/visual/captchas
- CAPTCHAs to verify a human user
- data-attributes/document-related/structural
- Document structure-related
- data-attributes/document-related/structural/running-titles
- Titles repeated each page
- data-attributes/document-related/structural/footnotes
- Footnotes at bottom of page
- data-attributes/document-related/structural/references
- Bibliographic references on page
- topic
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/economy
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/economy/financial
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/economy/financial/checks
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/economy/financial/invoices
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/economy/financial/bank-notes
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/maps
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/maps/topographical
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/maps/road
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/maps/land-use
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/traffic
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/traffic/number-plates
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/social-science/traffic/signs
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/architecture
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/architecture/floor-plans
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/architecture/drawings
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/medical
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/engineering-drawings
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/engineering/patents
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/media
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/media/adverts
-
Description coming soon.
- topic/computing
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups/admins
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups/workflow-experts
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups/domain-experts
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups/domain-experts/dia
-
Description coming soon.
- user-groups/domain-experts/librarians
-
Description coming soon.
|