Workflows
There are several steps necessary to get the fulltext of a scanned print. The whole OCR process is shown in the following figure:
The following instructions describe all steps of an OCR workflow. Depending on your particular print (or rather images), not all of those steps might be necessary to obtain good results. Whether a step is required or optional is indicated in the description of each step. This guide provides an overview of the available OCR-D processors and their required parameters. For more complex workflows and recommendations see the OCR-D-Website-Wiki. Feel free to add your own experiences and recommendations in the Wiki! We will regularly amend this guide with valuable contributions from the Wiki.
Note: In order to be able to run the workflows described in this guide, you need to have prepared your images in an OCR-D-workspace. We expect that you are familiar with the OCR-D-user guide which explains all preparatory steps, syntax and different solutions for executing whole workflows.
Image Optimization (Page Level)
At first, the image should be prepared for OCR.
Step 0.1: Image Enhancement (Page Level, optional)
Step 0.2: Font detection
Step 1: Binarization (Page Level)
Step 2: Cropping (Page Level)
Step 3: Binarization (Page Level)
For better results, the cropped images can be binarized again at this point or later on (on region level).
Available processors
| Processor | Parameter | Remark | Call | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ocrd-olena-binarize | Recommended | ocrd-olena-binarize -I OCR-D-CROP -O OCR-D-BIN2 |
||
| ocrd-sbb-binarize | -P model |
pre-trained models can be downloaded from [here](https://qurator-data.de/sbb_binarization/) or via the [OCR-D resource manager](https://ocr-d.de/en/models) | ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P model modelname |
|
| ocrd-skimage-binarize | ocrd-skimage-binarize -I OCR-D-CROP -O OCR-D-BIN2 |
|||
| ocrd-cis-ocropy-binarize | ocrd-cis-ocropy-binarize -I OCR-D-CROP -O OCR-D-BIN2 |
Step 4: Denoising (Page Level)
Step 5: Deskewing (Page Level)
Step 6: Dewarping (Page Level)
Layout Analysis
By now the image should be well prepared for segmentation.
Step 7: Region segmentation
Image Optimization (Region Level)
In the following steps, the text regions should be optimized for OCR.
Step 8: Binarization (Region Level)
In this processing step, a scanned colored /gray scale document image is taken as input and a black and white binarized image is produced. This step should separate the background from the foreground.
The binarization should be at least executed once (on page or region level). If you already binarized your image twice on page level, and have no large images, you can probably skip this step.
Available processors
| Processor | Parameter | Remarks | Call |
|---|---|---|---|
| ocrd-skimage-binarize | -P level-of-operation region |
ocrd-skimage-binarize -I OCR-D-SEG-REG -O OCR-D-BIN-REG -P level-of-operation region |
|
| ocrd-sbb-binarize | -P model -P operation_level region |
pre-trained models can be downloaded from [here](https://qurator-data.de/sbb_binarization/) or with the [OCR-D resource manager](https://ocr-d.de/en/models) | ocrd-sbb-binarize -I OCR-D-IMG -O OCR-D-BIN -P model modelname -P operation_level region |
| ocrd-preprocess-image |
-P level-of-operation region-P "output_feature_added" binarized-P command "scribo-cli sauvola-ms-split '@INFILE' '@OUTFILE' --enable-negate-output"
|
ocrd-preprocess-image -I OCR-D-SEG-REG -O OCR-D-BIN-REG -P level-of-operation region -P output_feature_added binarized -P command "scribo-cli sauvola-ms-split @INFILE @OUTFILE --enable-negate-output"
|
|
| ocrd-cis-ocropy-binarize | -P level-of-operation region-P "noise_maxsize": float |
ocrd-cis-ocropy-binarize -I OCR-D-SEG-REG -O OCR-D-BIN-REG -P level-of-operation region |
Step 9: Clipping (Region Level)
Step 10: Deskewing (Region Level)
In this processing step, text region images are taken as input and their skew is corrected by annotating the detected angle (-45° .. 45°) and rotating the image. Optionally, also the orientation is corrected by annotating the detected angle (multiples of 90°) and transposing the image.
|
|

|
Available processors
| Processor | Parameter | Remarks | Call |
|---|---|---|---|
| ocrd-cis-ocropy-deskew | -P level-of-operation region |
ocrd-cis-ocropy-deskew -I OCR-D-BIN-REG -O OCR-D-DESKEW-REG -P level-of-operation region |
|
| ocrd-tesserocr-deskew | Fast, also performs a decent orientation correction | ocrd-tesserocr-deskew -I OCR-D-BIN-REG -O OCR-D-DESKEW-REG |
Step 11: Line segmentation
Step 12: Resegmentation (Line Level)
Step 13: Dewarping (Line Level)
In this processing step, the text line images get vertically aligned if they are curved.
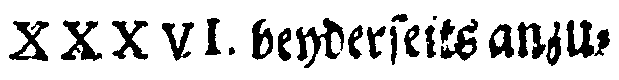
|
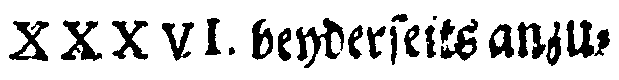
|
Available processors
| Processor | Parameter | Remarks | Call |
|---|---|---|---|
| ocrd-cis-ocropy-dewarp | ocrd-cis-ocropy-dewarp -I OCR-D-CLIP-LINE -O OCR-D-DEWARP-LINE |
Text Recognition
Step 14: Text recognition
Step 14.1: Font style annotation
Post Correction (Optional)
Step 15: Text alignment
Step 16: Post-correction
Evaluation (Optional)
If Ground Truth data is available, the OCR and layout recognition can be evaluated.
Step 17: Layout Evaluation
Step 18: OCR Evaluation
Generic Data Management (Optional)
OCR-D produces PAGE XML files which contain the recognized text as well as detailed information on the structure of the processed pages, the coordinates of the recognized elements etc. Optionally, the output can be converted to other formats, or copied verbatim (re-generating PAGE-XML)